Classification of Wave
Classification of Wave: Overview
This Topic covers sub-topics such as Transverse and Longitudinal Waves, Waves on String, Mechanical and Electromagnetic Waves, Classification of Wave Motion and, One, Two and Three Dimensional Waves
Important Questions on Classification of Wave
Energy is not propagated by which of the following waves?
What are the differences between mechanical and non-mechanical waves?
The waves in a string are transverse in nature.
For a three-dimensional wave represented by
The direction of is
Which one of the following is an example of a one-dimensional wave?
Which one of the following principles can be used to explain propagation of wave in two or three dimension?
For a three-dimensional wave of function and wave velocity , the equation for the wave can be given by
A uniform rope of mass and length hangs from a celling. The speed of transverse waves in the rope at a point at a distance from the lower and of the rope is
If tension of sonometer wire is made four times, then its frequency will change by a factor of:
A string of length has mass. The speed of the simple harmonic wave produced in it is . The tension in the string is
If the mass of long steel wire is then the speed of produced transverse waves on the wire under tension in the wire is
Two identical stones are dropped into opposite ends of a puddle. The waves created by the stones travel towards each other. What happens in the middle of the puddle?
Assertion: In longitudinal stationary waves, displacement node is pressure antinode and vice-versa.
Reason: At the point of displacement, node particles are at rest and variation in pressure is maximum.
The distance between two consecutive crests in a wave train produced in a string is . If complete waves pass through any point per second, the velocity of the wave is
A uniform string of length and mass is hung vertically. Find the speed of wave at the mid-point of the string :-
A uniform rope of length and mass hangs vertically from a rigid support. A block of mass is attached to the free end of the rope. A transverse pulse of wavelength is produced at the lower end of the rope. The wavelength of the pulse when it reaches the top of the rope will be-
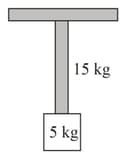
Both the strings, shown in figure are made of same material and diameter of is double that of . The pulleys are light. The speed of a transverse wave in the string is and in it is then is :